-
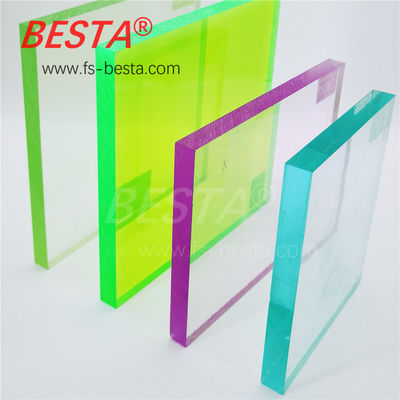
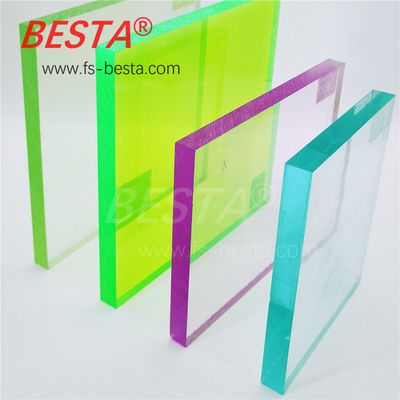
Cast Acrylic Sheets
-
Transparent Acrylic Sheets
-
Colored Acrylic Sheets
-
Acrylic Art Sculptures
-
Modern Acrylic Furniture
-
Light Guide Acrylic Sheet
-
Extruded Acrylic Sheet
-
Acrylic Diffuser Sheet
-
Double Layer Acrylic Sheet
-
Glitter Acrylic Sheet
-
Bubble Acrylic Sheet
-
Fireproof Acrylic Sheet
-
Clear Acrylic Bar
-
Clear Acrylic Hinges
-
Solid Acrylic Sphere
-
Mirror Acrylic Sheets
-
Decorative Acrylic Sheets
-
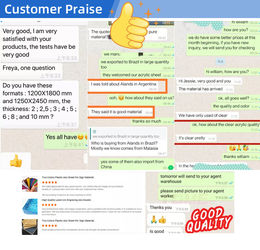 bensonI want to say that your products are very good. Thank you for all your suggestion, also good after sales service.
bensonI want to say that your products are very good. Thank you for all your suggestion, also good after sales service.
OEM PMMA Fireproof Acrylic Sheet Heat Resistant Plexiglass Sheets
| Place of Origin | China |
|---|---|
| Brand Name | BESTA |
| Certification | ITS, SGS, RoHS and REACH |
| Model Number | Acrylic Sheets |
| Minimum Order Quantity | 300KG |
| Price | USD3.8/KG |
| Packaging Details | Inner packing: Craft paper or PE film covered in both sides . Outer packing: Fumigation wooden Pallet ,Pallet size: same size as the acrylic sheet size |
| Delivery Time | 5~8 work days |
| Payment Terms | L/C, T/T |
| Supply Ability | 2000pcs/week |
| Material | PMMA Acrylic | Density | 1.20g/cm3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Certificate | ITS, SGS, RoHS And REACH | Color | White, Black, Red, Blue, Transparent, Translucent, Etc |
| Thickness | 2~50mm | Resistant | Excellent Resistance To Weather |
| Packing | Both Sides Covered By PE Film Or Craft Paper | ||
| Highlight | PMMA Fireproof Acrylic Sheet,PMMA Heat Resistant Plexiglass Sheets,OEM Fireproof Acrylic Sheet |
||
Acrylic sheets, also known as polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), are generally not considered fireproof. Acrylic is a thermoplastic material that has a relatively low ignition temperature and can melt or burn when exposed to high heat or flames. When acrylic sheets are subjected to fire, they can release smoke, toxic fumes, and dripping molten material.
However, there are fire-resistant or fire-retardant treatments available for acrylic materials that can improve their fire performance. These treatments are designed to slow down the spread of flames and reduce the release of smoke and hazardous gases.
Fire-resistant acrylic sheets are typically manufactured by incorporating fire-retardant additives into the acrylic resin during the production process. These additives work by interrupting the combustion process and reducing the flammability of the material. The specific additives and their concentrations may vary depending on the manufacturer and the desired fire rating.
Fire-resistant acrylic sheets are often classified based on their fire ratings, such as Class B, Class C, or Class A. Class A fire-rated acrylic sheets offer the highest level of fire resistance and are suitable for applications where strict fire codes and regulations must be met.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()